The actual performance of micro jobs (“microjobs”) by users of an online platform (“crowdworkers”) on the basis of a framework agreement concluded with its operator (“croudsourcer”) may result in the legal relationship qualifying as an employment relationship.
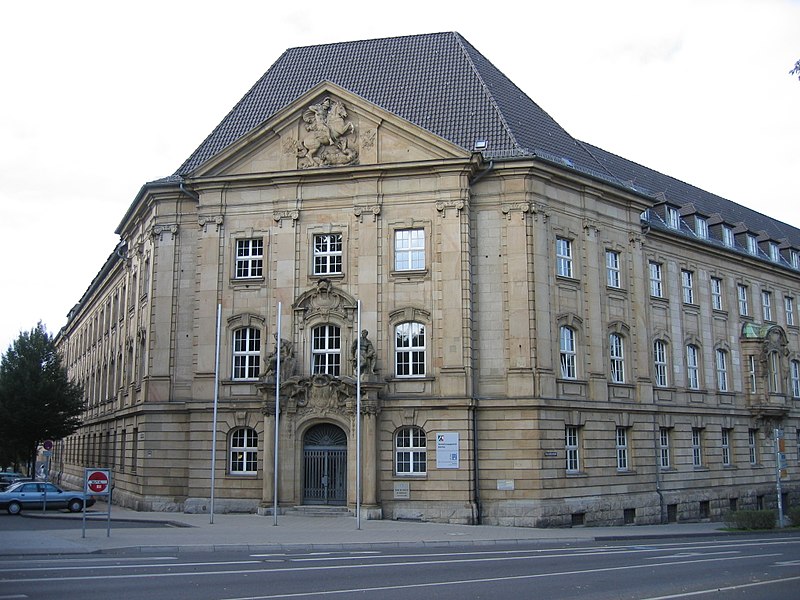
The defendant controls the presentation of branded products in retail stores and at service stations on behalf of its customers. It has the control activities themselves performed by crowdworkers.
Their task is, in particular, to take photos of the presentation of goods and answer questions about the promotion of products. On the basis of a “basic agreement” and general terms and conditions, the defendant offers the “microjobs” via an online platform. Via a personally set up account, each user of the online platform can accept orders related to specific points of sale without being contractually obligated to do so.
If the crowdworker takes on an assignment, he or she must regularly complete it within two hours according to the crowdsourcer’s detailed specifications. For completed missions he will be credited with experience points on his user account. The system increases the level with the number of completed orders and allows to accept several orders at the same time.
The plaintiff most recently performed 2978 orders for the defendant over a period of eleven months before it announced in February 2018 that it would not offer him any more orders to avoid future disagreements.
In his action, he first sought a declaration that an employment relationship of indefinite duration exists between the parties. In the course of the litigation, the defendant terminated any existing employment relationship on June 24, 2019, as a precautionary measure. Thereupon, the plaintiff filed his lawsuit, with which he also inter alia. compensation claims, has been extended to include a claim for protection against dismissal. The lower courts dismissed the action. They denied the existence of an employment relationship between the parties.
The plaintiff’s appeal was partially successful. The Ninth Senate of the Federal Labor Court recognized that the plaintiff was in an employment relationship with the defendant at the time of the precautionary termination of June 24, 2019.
Pursuant to Section 611a of the German Civil Code (BGB), the status of employee depends on the fact that the employee performs work that is subject to instructions and determined by others in a state of personal dependence. If the actual performance of a contractual relationship shows that it is an employment relationship, the designation in the contract is irrelevant.
The overall assessment of all circumstances required by law may show that crowdworkers are to be regarded as employees. It speaks for an employment relationship if the client controls the cooperation via the online platform operated by him in such a way that, as a result, the contractor cannot freely organize his activity in terms of place, time and content.
This is the case that was decided. The plaintiff performed work in a manner typical of an employee, bound by instructions and determined by others in personal dependence. It is true that he was not contractually obligated to accept offers from the defendant. However, the organizational structure of the online platform operated by the defendant was designed so that users registered and trained via an account continuously accept bundles of simple, step-by-step contractually specified small orders in order to complete them personally. Only a level in the rating system that increases with the number of jobs completed enables users of the online platform to accept several jobs at the same time in order to complete them on one route and thus, in effect, earn a higher hourly wage. Through this incentive system, the plaintiff was induced to continuously perform control activities in the district of his habitual residence.
The Ninth Senate of the Federal Labor Court nevertheless predominantly rejected the plaintiff’s appeal, since the precautionary termination effectively terminated the parties’ employment relationship. With regard to the claims for remuneration asserted by the plaintiff, the legal dispute was referred back to the Regional Labor Court. The plaintiff cannot without further ado demand payment of remuneration in accordance with the fees he previously received as a supposed freelancer.
If a supposedly freelance service relationship subsequently turns out to be an employment relationship, it cannot generally be assumed that the remuneration agreed for the freelancer was also agreed in terms of amount for employment as an employee. The usual remuneration within the meaning of the German Civil Code (HGB) is owed. § 612 para. 2 BGB, the amount of which the Regional Labor Court must clarify.