Account suspensions from online and mobile games
Playing online games or mobile games is becoming more and more fashionable and already the vast majority of Germans play...
Read moreDetailsThe digitization of larger sectors encounters organizational, technical and legal problems. The potential applications of blockchain technology offer a unified solution in almost all sectors of the economy. However, due to the relative newness of this technology, there is still largely a lack of clarity as to how blockchain can be applied in a meaningful and conflict-free manner. This paper focuses on providing a broad overview of DLT and its potential when used correctly.
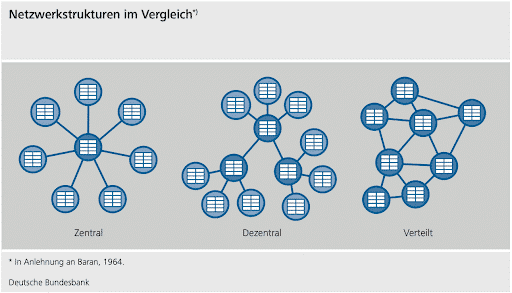
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a decentralized digital transaction recording system that aims to establish consensus among decentralized databases. Decentralized means that the write permission does not lie with one instance, but is distributed over several instances. It allows all network participants to share write, read and save permissions. Transactions are verified and confirmed in a decentralized manner by network participants, eliminating the need for a third party to manage the account.
Blockchain is a subset of DLT. Blockchain describes a data structure that irrevocably stores the transaction history, whereas DLT additionally describes the data structure across multiple locations.
With its digital network structure and simultaneous access to a common database, DLT promises higher levels of transparency, operational efficiency, security and resilience, independence from intermediaries, and automation in settlement. DLT thus solves problems of conventional data backup systems. Its main advantages can be summarized as follows:
In order to ensure the integrity and stability of the financial markets even under changing environmental conditions, requirements of the supervisory authorities, such as BaFin, must be complied with. Thus, the question still remains as to how requirements for IT security, data protection or consumer protection can be fully ensured when integrating blockchain systems. Only legally sound texts and the legal advice of a specialist lawyer can overcome the high legal hurdles in individual cases without conflict. The most common legal issues arise as follows:
The application of DLT is conceivable in almost all areas due to its efficiency. However, it is particularly interesting for financial sectors, logistics, open science, healthcare and public administration.
DLT brings important new features that can create significant changes in the global world market. Provided that your functions are not fundamentally misused, some basic legal points such as data protection and security must nevertheless be observed. Anyone who has discovered the potential of DLT and wants to take advantage of the fruits of this technology for their company at an early stage should act in a legally secure manner. As a specialist in blockchain and corporate law, I will guide you as a lawyer and as a business consultant, guiding you past the big and small obstacles to efficiently achieve your vision.
Do you still have questions about the use and risk assessment of DLT? I will be happy to advise you. Arrange a free initial consultation right away. I look forward to hearing from you.
Marian Härtel ist Rechtsanwalt und Fachanwalt für IT-Recht mit einer über 25-jährigen Erfahrung als Unternehmer und Berater in den Bereichen Games, E-Sport, Blockchain, SaaS und Künstliche Intelligenz. Seine Beratungsschwerpunkte umfassen neben dem IT-Recht insbesondere das Urheberrecht, Medienrecht sowie Wettbewerbsrecht. Er betreut schwerpunktmäßig Start-ups, Agenturen und Influencer, die er in strategischen Fragen, komplexen Vertragsangelegenheiten sowie bei Investitionsprojekten begleitet. Dabei zeichnet sich seine Beratung durch einen interdisziplinären Ansatz aus, der juristische Expertise und langjährige unternehmerische Erfahrung miteinander verbindet. Ziel seiner Tätigkeit ist stets, Mandanten praxisorientierte Lösungen anzubieten und rechtlich fundierte Unterstützung bei der Umsetzung innovativer Geschäftsmodelle zu gewährleisten.
Playing online games or mobile games is becoming more and more fashionable and already the vast majority of Germans play...
Read moreDetailsThe Higher Regional Court of Hamm has ruled that manufacturer's warranty statements in operating instructions can give rise to a...
Read moreDetailsNo majority for proposal to combat cybercrime A bill from Bavaria to combat cybercrime was voted on in plenary on...
Read moreDetailsAs I have pointed out several times in posts, the risk of running into the warning trap, especially from young,...
Read moreDetailsFor many companies, self-employed persons and freelancers, there is now or will soon be an obligation to record the contact...
Read moreDetailsTikTok: An overview TikTok is the world's fastest growing platform for creatives. There are several ways to become an influencer...
Read moreDetailsToday, the new "Law on Strengthening Fair Competition" came into force, but in the opinion of many colleagues, it does...
Read moreDetailsSince it came into force in May 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has placed considerable demands on companies...
Read moreDetailsIn online retailing, the issue of the right of withdrawal is actually dead in the water. Anyone who sells products...
Read moreDetailsNo-code and low-code platforms enable rapid software development without extensive manual programming. Applications are increasingly being developed on the basis...
Read moreDetailsIn this insightful episode of the ITmedialaw podcast, we take an in-depth look at the intersection of Web3, blockchain...
Read moreDetailsIn this video, I talk a bit about transparent billing and how I communicate what it costs to work with...
Read moreDetails